US-based medical device company Checkpoint Surgical has introduced Checkpoint Gemini, a bipolar nerve stimulator intended to provide precise stimulation.
The single-use, sterile device is designed for providing electrical stimulation of exposed motor nerves or muscle tissue for locating and identifying nerves, as well as testing the nerve and excitability of the muscle.
It is an addition to the company’s Checkpoint nerve stimulator portfolio, which includes Checkpoint Intraoperative Stimulators, the Checkpoint Edge Nerve Cutting Kit and the Neuroshield Chitosan Membrane.
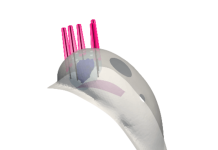
The Checkpoint Gemini nerve stimulator provides a bipolar stimulation probe for finely controlled stimulation, even at the fascicular level.
It aims to offer better clarity for surgeons to determine which of a nerve’s fascicles is responsible for a particular response.
Checkpoint Surgical president and CEO Derek Lewis said: “This expansion of Checkpoint Surgical’s stimulator portfolio ensures that we provide the surgeon with the optimal solution for clinical nerve procedures.
RELATED: Stryker Announces Launch of Q Guidance System with Spine Guidance Software
“Checkpoint Gemini complements our existing stimulators with a device optimised for precise nerve surgeries.”
Checkpoint Surgical said the device’s precision is made possible by its bipolar probe design, which focuses the energy delivered into a small area.
The device’s focused stimulation at 32Hz provides a tetanic muscle response, even on fast-twitch muscle tissue such as that found in the face or paediatric anatomy.
In addition, its biphasic waveform provides safe, continuous nerve activation without diminished response.
Similar to the Checkpoint Guardian, the nerve stimulator offers visual confirmation of stimulation delivery and a precise LCD status indicator of amplitude and pulse duration.
In July this year, Checkpoint Surgical introduced its Checkpoint Edge Nerve Cutting Kit.
The Checkpoint Edge Nerve Cutting Kit uses circumferential constraint to maintain the nerve’s natural shape during transection.
This can help prevent sliding, flattening or potential subsequent nerve edge malformation.
Are you Hiring?